Home / Training / Manuals / Atlas of breast cancer early detection / Cases
Atlas of breast cancer early detection
Go back to the list of case studies
.png) Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
| Case number: | 066 |
| Age: | 58 |
| Clinical presentation: | Postmenopausal woman with average risk of developing breast cancer presented with a lump in the right breast noticed on breast self-examination. |
Mammography:
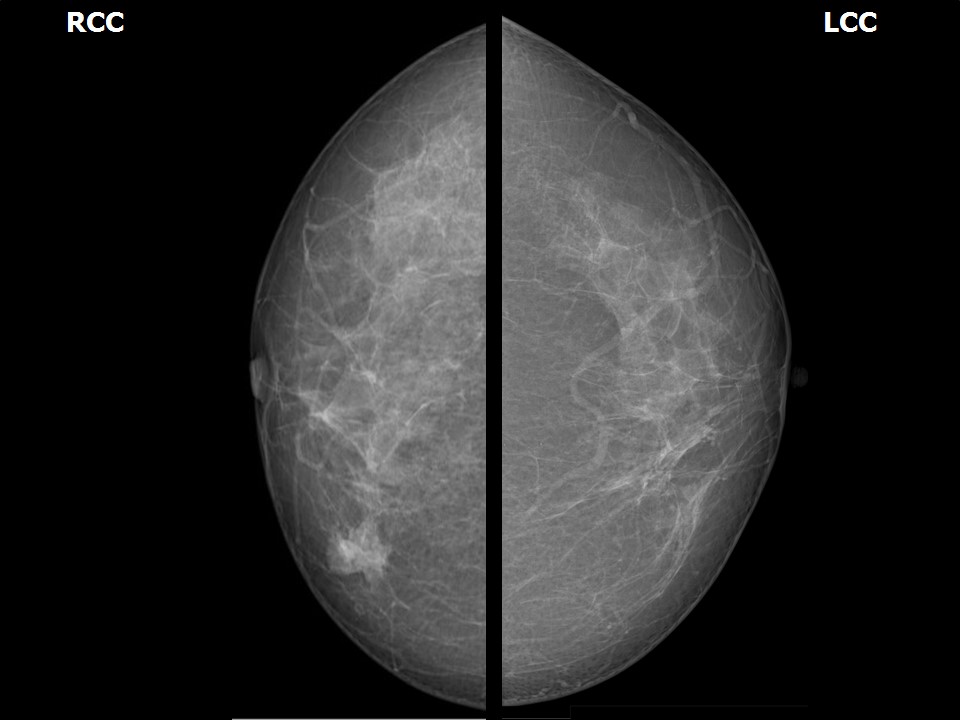
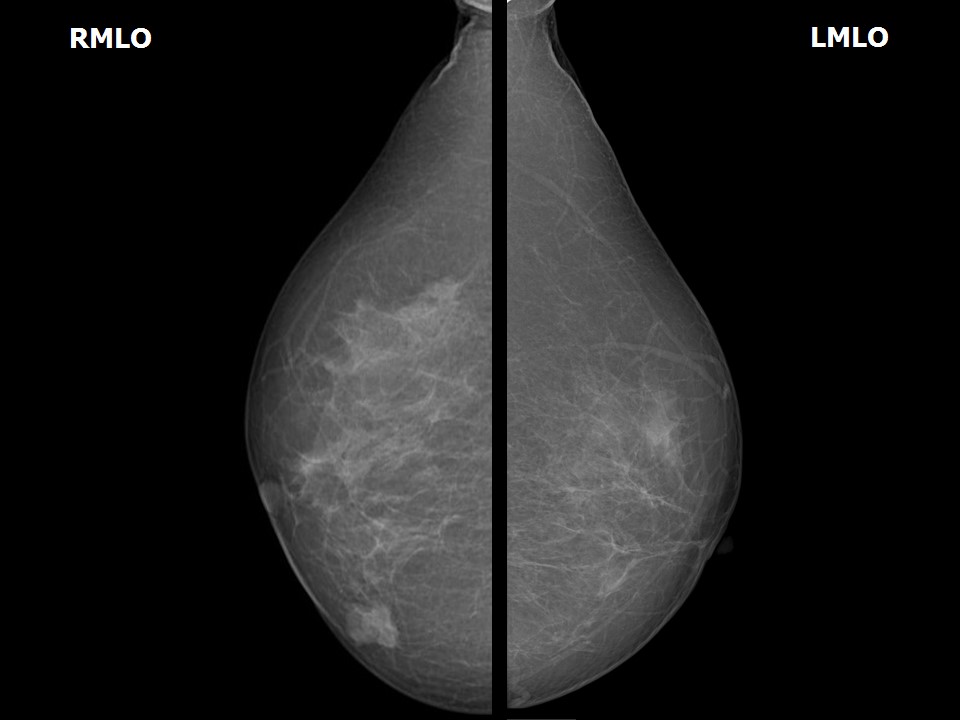
| Breast composition: | ACR category a (the breasts are almost entirely fatty) | Mammography features: |
| ‣ Location of the lesion: | Right breast, lower inner quadrant at 5 o’clock, anterior third |
| ‣ Mass: | |
| • Number: | 1 |
| • Size: | 1.8 × 1.5 cm |
| • Shape: | Oval |
| • Margins: | Partly circumscribed and partly indistinct |
| • Density: | High |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | None |
| • Suspicious: | None |
| • Distribution: | None |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | None |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | None |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | None |
| ‣ Skin lesion: | None |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | None |
Ultrasound:
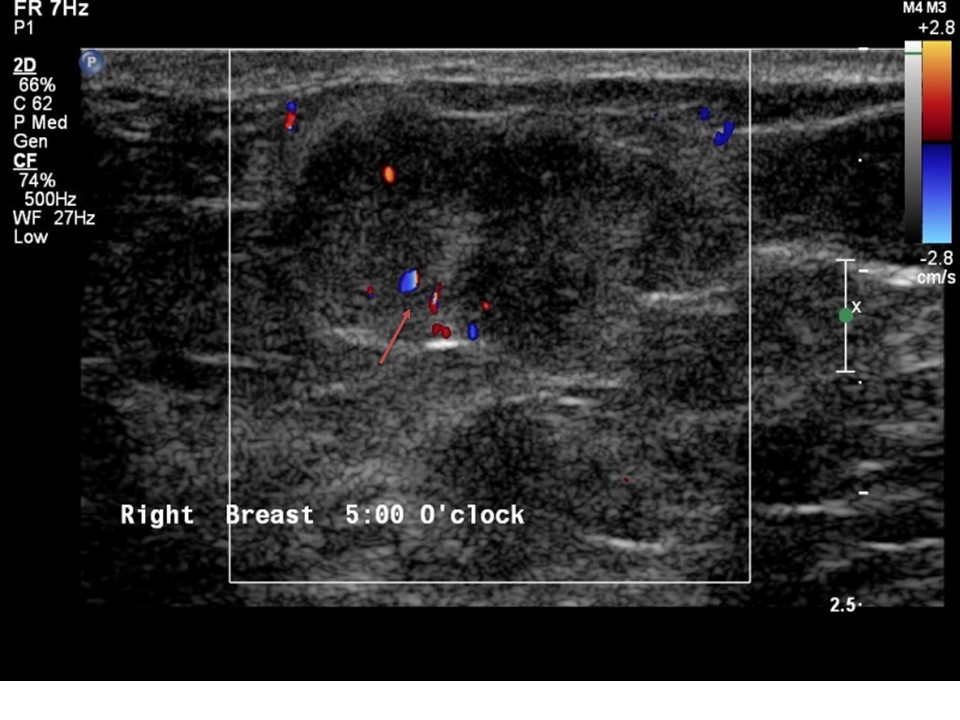
| Ultrasound features: Right breast, lower inner quadrant 5 o’clock position | |
| ‣ Mass | |
| • Location: | Right breast, lower inner quadrant 5 o’clock position |
| • Number: | 1 |
| • Size: | 2.0 × 1.2 cm |
| • Shape: | Irregular |
| • Orientation: | Parallel |
| • Margins: | Partly circumscribed and partly indistinct margins |
| • Echo pattern: | Isoechoic |
| • Posterior features: | No posterior features |
| ‣ Calcifications: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | Internal vascularity |
| ‣ Special cases: | None |
BI-RADS:
BI-RADS Category: 4B (moderate suspicion of malignancy)Further assessment:
Further assessment advised: Referral for cytologyCytology:
| Cytology features: | |
| ‣ Type of sample: | FNAC (solid lesion) |
| ‣ Site of biopsy: | |
| • Laterality: | Right |
| • Quadrant: | Lower inner |
| • Localization technique: | Palpation |
| • Nature of aspirate: | Very transparent sticky material aspirated |
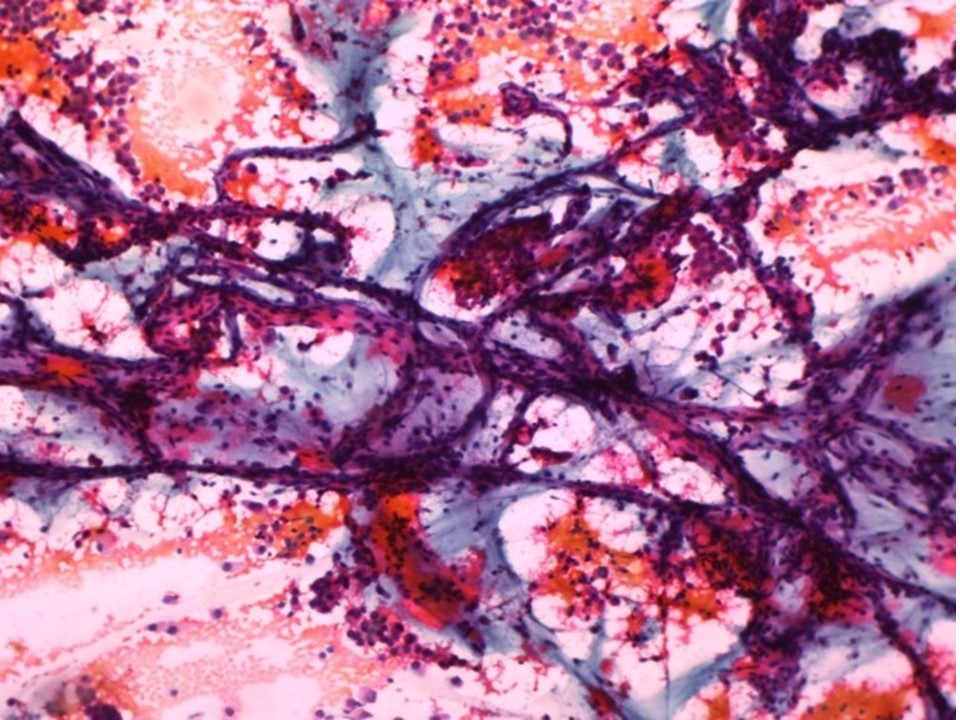
| ‣ Cytological description: | Smears show loosely cohesive and many single isolated malignant cells with round nuclei. The background shows mucinous material. Branching capillary structures are also seen |
| ‣ Reporting category: | Malignant |
| ‣ Diagnosis: | Mucinous carcinoma |
| ‣ Comments: | Pitfalls: The appearance of malignant cells in colloid carcinoma is often low grade, requiring careful exclusion of other benign entities with mucinous features, such as mucocele and fibroadenoma with abundant mucinous stroma |
Histopathology:
Breast-conserving surgery
| Histopathology features: | |
| ‣ Specimen type: | Breast-conserving surgery |
| ‣ Laterality: | Right |
| ‣ Macroscopy: | Cut surface shows an irregular tumour (1.5 × 1.5 × 1.2 cm) with glistening gelatinous areas, soft in consistency |
| ‣ Histological type: | Mucinous carcinoma |
| ‣ Histological grade: | Grade 1 (2 + 2 + 1 = 5) |
| ‣ Mitosis: | 5 |
| ‣ Maximum invasive tumour size: | 1.7 cm in greatest dimension |
| ‣ Lymph node status: | 0/30 |
| ‣ Peritumoural lymphovascular invasion: | Present |
| ‣ DCIS/EIC: | Not identified |
| ‣ Margins: | Free of tumour |
| ‣ Pathological stage: | pT1cN0 |
| ‣ Biomarkers: | |
| ‣ Comments: |
Case summary:
| Postmenopausal woman presented with lump in the right breast. Diagnosed as right breast mass of suspicious morphology, BI-RADS 4B on imaging, as mucinous carcinoma on cytology, and as mucinous carcinoma, pT1cN0 on histopathology. |
Learning points:
|